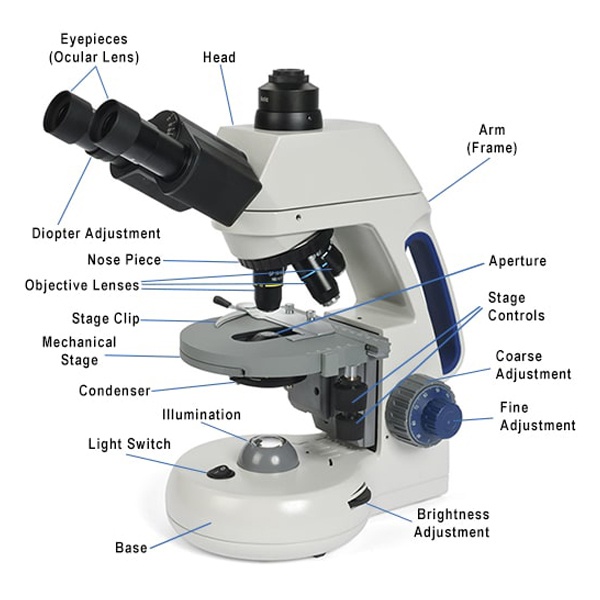
Labeled Diagram That Explains The Function Of Compound Light Microscope.” Labeled diagrams are a very common way to help students identify the different parts of a microscope and understand. to disambiguate all components. Compound Light Microscope lInstrument TAGGED provides students and researchers with illustration of how the microscope operates in conjunction with ascending light to bring small objects into focus. No matter if in the study hall or lab, a Compound Light Microscope Labeled lifts studying about structure and function. Labeled Compound Light Microscope is very important for a proper usage. Each piece serves its own purpose in terms of zoom and precision. In this article, you can get to know the named parts of a microscope. Getting to know these parts will help you use the microscope effectively.
But whether you’re a student or an enthusiast of science, it is vital to gain a firm grasp on the microscope’s parts. Let us discuss about the labelled parts and their functions. You will use this information on your scientific explorations and studies.
Introduction To Compound Light Microscope
Biology labs across the world have a compound light microscope on their shelves. It is allows us to investigate the small world of cells and microorganisms. It employs lenses and light in the visible spectrum to enlarge small objects. Scientists and students use it to do biology and chemistry.
Understanding its parts is essential. A labeled microscope exposes its parts. Each part has a specific role in magnification and resolution. Here’s a little on the history and what makes this precious device significant.
Basic Concept About Microscope
Take microscopes with compound lenses, for example. These lenses magnify things in increments. The objective is positioned next to the specimen. It provides the primary magnification. The eyepiece lens magnifies the enlarged image still further.
Light passes through the specimen. It travels up through the lens. Such light is useful for forming a clear image of the object. The base of the microscope supports this action. It consists of a arm which links the lenses to the base. The platform secures the specimen in headset.
Microscope Importance In Scientific Research
Microscopes are indispensable for scientific research. They turn on the radio so we can see cells and tissues. This can be useful for disease understanding. Bacteria and viruses can be viewed on microscopes.
They’re in education, where they show students the structures of cells. They foster curiosity and learning. Scientific discoveries have been made possible through the lens of a microscope. This instrument continues to be essential for expanding our understanding.
Parts of a Compound Light Microscope If you need help identifying the parts of a compound light microscope and their functions, this page can help.
The compound light microscope contains several parts such as the eyepiece, objective lenses, and stage. These parts aid in the enlargement and inspection of samples. The light and iris control are used to adjust the amount of light to enable viewing.
On the first look, understanding the compound light microscope parts appears like an insurmountable mountain to a new student of microscopy. But it can be a little overwhelming at first, breaking it down into its optical and mechanical components helps you easily understand how this amazing tool operates. Whether you’re in school, an amateur or delving into a new field, understanding these parts can benefit your microscopic explorations.
Optical Parts of Microscope
An Explanation of the Parts of a Compound Light Microscope The optical components of compound light microscopes are necessary to magnify specimens. The ocular lens that you can place your eye against to look at the sample is called the eyepiece. These objective lenses are the primary source of magnification for your specimen and will be a 10x power. They are available in various types of powers ranging from 4x to 10x 40x and up to100x these lenses are attached on a revolving nosepiece where one can change it easily. The stage clips secure the slide in position. This keeps your sample still as you view it.
The condenser projects light concentrated on the specimen. It is installed immediately below the stage and frequently contains an adjustable diaphragm to regulate the intensity of light. The lighting is typically from an integral bulb that illuminates the sample from underneath. If you are having trouble seeing your specimen, try increasing or decreasing the light.
Optical System
Labeled diagram of a compound light microscop A great explanation and labeled parts. It consists of the eyepiece, the objective lens, stage and condenser. Every part has its function to magnify small objects for closer inspection.
The optical system of a compound light microscope is where all the magic happens. It is the core of the microscope, and its where you can see little things that would not usually be visible to the unaided eye. By mastering this system, you can open up a whole new world of microworld exploration. Imagine being able to watch a single cell in a leaf, or a drop of pond water. The experience starts with the optical system – finely-tuned optics that magnify and resolve images accurately.
Eyepiece
Your eyepiece (ocular lens) is what you peek through to see the world in minutiae. It is the lens with which you look through at the top of the microscope. Usually, the image is then magnified by another 10x or so. An eyepiece can be the difference between a wonderful or mediocre view. Ever wonder why some microscopes give you a clear picture, while others seem fuzzy? The eyepiece is often what sets the quality apart. When choosing an eyepiece, think about comfort and quality. Some eyepieces have adjustable diopters, which means you can fine-tune the focus to match your vision.
Objective Lenses
The objective lenses are the nearest to the sample and are in fact where most of magnification occurs. Nearly all microscopes are equipped with several objective lenses on a rotating nosepiece. This configuration will allow you to change the magnification quickly and usually go from 4x to 100x (most times it ranges around here). Have you ever tried looking at a tiny insect wing or taking a close up of a plant cell? The objective lens is what determines how much detail you can see. Higher magnification means finer detail, but it needs more light (more resolution) and focus precision. Whenever possible, try to color-code objective lenses so you can easily identify their magnification strength. Although it is a scope that has been recommended when shopping for a quality microscope try to get one with high numerical aperture objectives as they yield better resolution and clarity.
Knowing the optical system, which entails the eyepiece and the objective lenses, can transform your microscopy abilities. What is something you’ve seen under a microscope that totally awed you? Let me know about your culture and things you have found as you dig deeper into the microscopic universe.
Illumination System
The illumination system for a compound light microscope consists of the light source, condenser and diaphragm. Such a system senses crisp and bright images of the specimen. Distinguish each part easily with convenient labeling.
The lighting arrangement in a light microscope is critical to the observation of small specimens. This mechanism provides bright field illumination when the specimen itself has high light absorption characteristics, and enables detailed observation of structures. Understanding how this system operates can increase the proficiency of your microscopy.
Light Source
The light source forms the core of the lighting system. Today’s microscopes generally use LED lights, which are bright and energy-efficient. And what happens if you’re trying to look at a tiny insect wing lacking sufficient light? it’s extremely difficult. But with a decent light source, every vein shows up, as if you are looking at an intricate map close up. The difference in light intensity makes for such a simple yet powerful change. It can bring out features you might not otherwise see: Try adjusting the dimmer switch in your living room to create some ambiance. It’s a similar concept, but for science.
Labeled Diagram of a Compound Light Microscope With A Focus Mechanism Is shown belowFYI.
A compound-light microscope is a valuable piece of equipment for magnifying small objects. The cohering and de-focusing of the images needs to be absolutely tight. This permits users to change the distance between the lenses and the object. This system ensures that the object is sharp in focus.
Coarse Adjustment
The “coarse” focusing knob is the bigger of the two. The stage goes up and down rapidly. This aids in finding the specimen under the microscope objectives. First it is used to make general focus adjustments. Rotating it lets you locate the general point of interest.
It is very useful to make an initial focusing especially at the lowest power level. Be especially careful when using it so you don’t crack the slide or break a specimen.
Fine Adjustment
The fine adjustment to the knob is minor and even finer. It refines the focus after using the coarse adjustment. It displaces the stage slowly to focus on the details. This is important to be able to view fine details at higher magnifications.
Noble fine adjustment clear and accurate picture GODSPEED! Then, turn it slowly for the finest focussing point.

Microscope Stage and Specimen Handling
Knowing how to work with specimens is key for anyone beginning on a compound light microscope. A major player in this process is the stage, where the slide will sit. Proper treatment lets you observe your specimen clearly. So let’s get down to the basics of the stage and how best to handle your specimens.
Stage Clips
Use stage clips which help to stabilize slides. They anchor the slide in position, so you can concentrate without lack of stability. Think about trying to read a slide and it’s shaking – annoying, right? These clips prevent that.
Did you ever try to balance a slide on an uneven surface? Because stage clips function as a dependable set of hands, gripping the slide securely. This is particularly important if you’re dealing with multiple slides and want them transitioning fast. The clips are strong enough to keep your slides safely in place while you switch.
Stage Controls
Stage controls are the way you make your way around. They let you move the slide directly under the objective. It’s as if you had a GPS for your specimen to lead you to the part that you want to look at.” It’s as if you’ve glimpsed something interesting, but can’t quite get your hands (or eyes) on it. Stage controls save the day.
These controls are not just about movement; they’re about precision. They allow you to make micro-adjustments, that mean the difference between being able to spot critical details or not. Ever find something unexpected in adjusting the stage? That’s how fine-tuning your perspective pays.
Just imagine, if only you could explore the entirety of your specimen with ease… Stage controls let you enjoy that freedom by making your trip a smooth and comfortable exploration.
COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE CARE OF THE MICROSCOPE
The compound light microscope is a vital tool in laboratories. Proper use and care extend its lifespan. Regular maintenance ensures clear, accurate results. Let’s explore daily care and long-term storage tips. These practices will keep your microscope in top condition.
Everyday Use: On Compound Light Microscope Labeled
Protect your lenses for clearer vision and better protection on the job. Dry the lenses with a soft, lint-free cloth. For stubborn spots, wash with lens cleaning solution. Avoid touching lenses with fingers. Fingerprints blur images. Check light source regularly. Replace bulbs when dim. Position the light for best viewing. Don’t let it get too dirty or covered with crap. The clean stage makes a slide move easily.
Long-term Storage
Proper storage protects the microscope. Keep in dust free room. And, when not in use, protect it with a dust jacket. Keep it in a dry area. Humidity can damage optical parts. Use a case to transport it. This prevents knocks and scratches. Check if the case is padded for protection. Keep the microscope locked when not in use. This prevents unauthorized handling. With regular checks, it can stay in a good condition.
Common Applications
A labeled diagram of a compound light microscope helps students understand the various parts. It’s also used in schools and laboratories. This device enlarges tiny objects and renders details visible for scientific observations.
The compound microscope can be a useful instrument in several fields of science. Recognising its usual uses can increase your appreciation of its worth. Whether you’re a student, a scholar or just curious, understanding where and how it’s used can help enhance your appreciation of its significance. Further here are some interesting uses.
Biological Studies
The most common use of compound microscopes is biological research. Such microscopes help scientists get a close-up view of cells, tissues and tiny organisms. Picture yourself looking into the microcosmic realm and finding life’s secret nuances. You will remember (from high school biology) that first excited glimpse of a cell dividing when you looked down the lens of a microscope in biology class. Such visual revelations are essential in understanding diseases and constructing treatments. What ancient questions of cellular life might you answer with a microscope?
Compound Light Microscope in Material Science Labelled diagram of x Use ‘ Click here for mobile version.
Compound light microscopes are for more than biology. They’re also material scientists of sorts. Scientists employ these microscopes to explore the microstructure of metals, polymers and other materials. This is of assistance in understanding material behavior and product design. Consider the smartphone in your hand. This was constructed using high quality materials,probably had a micro-scope used to examine the materials for strength and function. What kind of innovative things would you be able to do with advanced knowledge in material science. Some uses of Compound Light Microscopes The following are some general uses of the compound light microscopes that have made them important in scientific progression. As you think about these fields, consider how you could interface with this technology. Where in your work or study do you see potential for discovery?
Frequently Asked Questions
What Exactly is a compound light microscope?
The compound light microscope uses two or more lenses to produce an enlarged image.
How does a light microscope work?
It directs the light through lenses to amplify a small object so that it can be seen.
What is the magnitude of a simple light microscope in compound microscope?
It’s standard for being able to magnify images of objects up in the 40x-1000x range.
Can you describe the major components of a compound light microscope.
Main components are the eyepiece, objective lens, stage and light source.
How is a light microscope different from an electron microscope?
This is because light microscopes use visible light, while electron microscopes use electrons.
What are the uses of compound light microscope?
It’s user friendly, inexpensive and great for viewing live specimens.
Are bacteria visible with a compound light microscope?
Yes it can see some bacteria, but you will need more magnification to do a bit of detail.
Conclusion About Microscope
The Details of the Compound Light Microscope A compound light microscope shows you a whole lot to explore. Each part plays a vital role. Knowledge of these elements helps you become a better microscopist. The eyepiece, Objective lenses, and Stage are important. They concentrate and amplify your samples. The illuminator sheds light, so you see those little things in full.
It’s those little tweaks that really count! Mastery of the fundamentals adds to your confidence. This is the backdrop against which these things rationalize. You can now view microcosmic organisms with the bare eyes. And what are to be found in this world of little are just waiting for you! Read on to find out more about this interesting tool.
It’s the beginning of your trip into the microcosm.
Labeled Diagram That Explains The Function Of Compound Light Microscope.” Labeled diagrams are a very common way to help students identify the different parts of a microscope and understand. to disambiguate all components. Compound Light Microscope lInstrument TAGGED provides students and researchers with illustration of how the microscope operates in conjunction with ascending light to bring small objects into focus. No matter if in the study hall or lab, a Compound Light Microscope Labeled lifts studying about structure and function. Labeled Compound Light Microscope is very important for a proper usage. Each piece serves its own purpose in terms of zoom and precision. In this article, you can get to know the named parts of a microscope. Getting to know these parts will help you use the microscope effectively.
But whether you’re a student or an enthusiast of science, it is vital to gain a firm grasp on the microscope’s parts. Let us discuss about the labelled parts and their functions. You will use this information on your scientific explorations and studies.
Introduction To Compound Light Microscope
Biology labs across the world have a compound light microscope on their shelves. It is allows us to investigate the small world of cells and microorganisms. It employs lenses and light in the visible spectrum to enlarge small objects. Scientists and students use it to do biology and chemistry.
Understanding its parts is essential. A labeled microscope exposes its parts. Each part has a specific role in magnification and resolution. Here’s a little on the history and what makes this precious device significant.
Basic Concept About Microscope
Take microscopes with compound lenses, for example. These lenses magnify things in increments. The objective is positioned next to the specimen. It provides the primary magnification. The eyepiece lens magnifies the enlarged image still further.
Light passes through the specimen. It travels up through the lens. Such light is useful for forming a clear image of the object. The base of the microscope supports this action. It consists of a arm which links the lenses to the base. The platform secures the specimen in headset.
Microscope Importance In Scientific Research
Microscopes are indispensable for scientific research. They turn on the radio so we can see cells and tissues. This can be useful for disease understanding. Bacteria and viruses can be viewed on microscopes.
They’re in education, where they show students the structures of cells. They foster curiosity and learning. Scientific discoveries have been made possible through the lens of a microscope. This instrument continues to be essential for expanding our understanding.

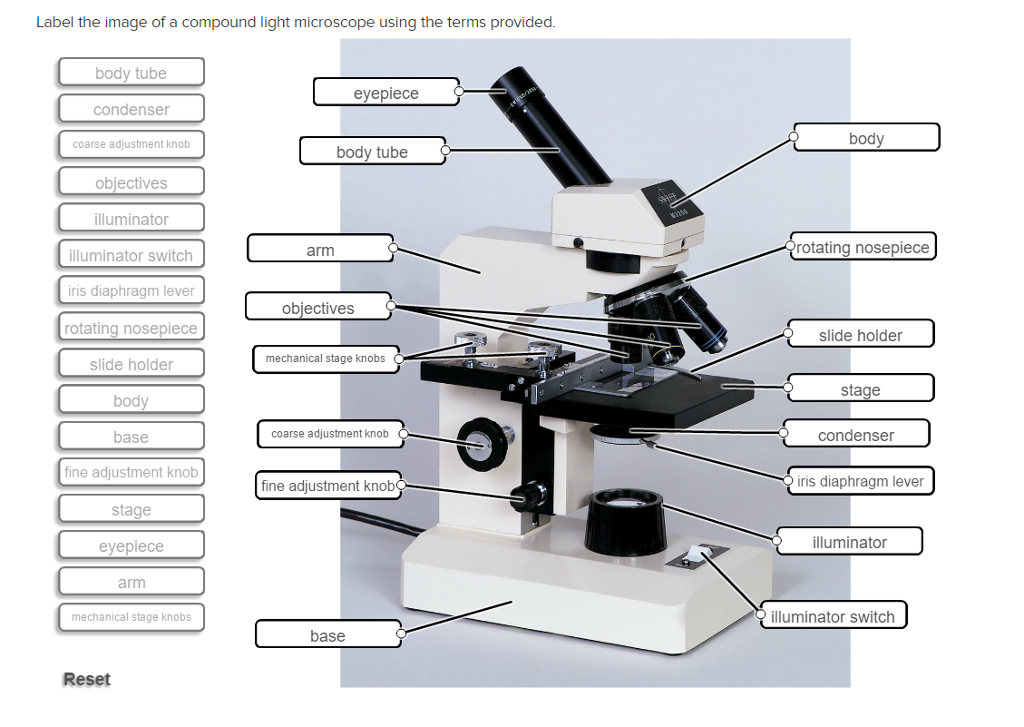
Parts of a Compound Light Microscope If you need help identifying the parts of a compound light microscope and their functions, this page can help.
The compound light microscope contains several parts such as the eyepiece, objective lenses, and stage. These parts aid in the enlargement and inspection of samples. The light and iris control are used to adjust the amount of light to enable viewing.
On the first look, understanding the compound light microscope parts appears like an insurmountable mountain to a new student of microscopy. But it can be a little overwhelming at first, breaking it down into its optical and mechanical components helps you easily understand how this amazing tool operates. Whether you’re in school, an amateur or delving into a new field, understanding these parts can benefit your microscopic explorations.
Optical Parts of Microscope
An Explanation of the Parts of a Compound Light Microscope The optical components of compound light microscopes are necessary to magnify specimens. The ocular lens that you can place your eye against to look at the sample is called the eyepiece. These objective lenses are the primary source of magnification for your specimen and will be a 10x power. They are available in various types of powers ranging from 4x to 10x 40x and up to100x these lenses are attached on a revolving nosepiece where one can change it easily. The stage clips secure the slide in position. This keeps your sample still as you view it.
The condenser projects light concentrated on the specimen. It is installed immediately below the stage and frequently contains an adjustable diaphragm to regulate the intensity of light. The lighting is typically from an integral bulb that illuminates the sample from underneath. If you are having trouble seeing your specimen, try increasing or decreasing the light.
Optical System
Labeled diagram of a compound light microscop A great explanation and labeled parts. It consists of the eyepiece, the objective lens, stage and condenser. Every part has its function to magnify small objects for closer inspection.
The optical system of a compound light microscope is where all the magic happens. It is the core of the microscope, and its where you can see little things that would not usually be visible to the unaided eye. By mastering this system, you can open up a whole new world of microworld exploration. Imagine being able to watch a single cell in a leaf, or a drop of pond water. The experience starts with the optical system – finely-tuned optics that magnify and resolve images accurately.
Eyepiece
Your eyepiece (ocular lens) is what you peek through to see the world in minutiae. It is the lens with which you look through at the top of the microscope. Usually, the image is then magnified by another 10x or so. An eyepiece can be the difference between a wonderful or mediocre view. Ever wonder why some microscopes give you a clear picture, while others seem fuzzy? The eyepiece is often what sets the quality apart. When choosing an eyepiece, think about comfort and quality. Some eyepieces have adjustable diopters, which means you can fine-tune the focus to match your vision.
Objective Lenses
The objective lenses are the nearest to the sample and are in fact where most of magnification occurs. Nearly all microscopes are equipped with several objective lenses on a rotating nosepiece. This configuration will allow you to change the magnification quickly and usually go from 4x to 100x (most times it ranges around here). Have you ever tried looking at a tiny insect wing or taking a close up of a plant cell? The objective lens is what determines how much detail you can see. Higher magnification means finer detail, but it needs more light (more resolution) and focus precision. Whenever possible, try to color-code objective lenses so you can easily identify their magnification strength. Although it is a scope that has been recommended when shopping for a quality microscope try to get one with high numerical aperture objectives as they yield better resolution and clarity.
Knowing the optical system, which entails the eyepiece and the objective lenses, can transform your microscopy abilities. What is something you’ve seen under a microscope that totally awed you? Let me know about your culture and things you have found as you dig deeper into the microscopic universe.
Illumination System
The illumination system for a compound light microscope consists of the light source, condenser and diaphragm. Such a system senses crisp and bright images of the specimen. Distinguish each part easily with convenient labeling.
The lighting arrangement in a light microscope is critical to the observation of small specimens. This mechanism provides bright field illumination when the specimen itself has high light absorption characteristics, and enables detailed observation of structures. Understanding how this system operates can increase the proficiency of your microscopy.
Light Source
The light source forms the core of the lighting system. Today’s microscopes generally use LED lights, which are bright and energy-efficient. And what happens if you’re trying to look at a tiny insect wing lacking sufficient light? it’s extremely difficult. But with a decent light source, every vein shows up, as if you are looking at an intricate map close up. The difference in light intensity makes for such a simple yet powerful change. It can bring out features you might not otherwise see: Try adjusting the dimmer switch in your living room to create some ambiance. It’s a similar concept, but for science.
Labeled Diagram of a Compound Light Microscope With A Focus Mechanism Is shown belowFYI.
A compound-light microscope is a valuable piece of equipment for magnifying small objects. The cohering and de-focusing of the images needs to be absolutely tight. This permits users to change the distance between the lenses and the object. This system ensures that the object is sharp in focus.
Coarse Adjustment
The “coarse” focusing knob is the bigger of the two. The stage goes up and down rapidly. This aids in finding the specimen under the microscope objectives. First it is used to make general focus adjustments. Rotating it lets you locate the general point of interest.
It is very useful to make an initial focusing especially at the lowest power level. Be especially careful when using it so you don’t crack the slide or break a specimen.
Fine Adjustment
The fine adjustment to the knob is minor and even finer. It refines the focus after using the coarse adjustment. It displaces the stage slowly to focus on the details. This is important to be able to view fine details at higher magnifications.
Noble fine adjustment clear and accurate picture GODSPEED! Then, turn it slowly for the finest focussing point.

Microscope Stage and Specimen Handling
Knowing how to work with specimens is key for anyone beginning on a compound light microscope. A major player in this process is the stage, where the slide will sit. Proper treatment lets you observe your specimen clearly. So let’s get down to the basics of the stage and how best to handle your specimens.
Stage Clips
Use stage clips which help to stabilize slides. They anchor the slide in position, so you can concentrate without lack of stability. Think about trying to read a slide and it’s shaking – annoying, right? These clips prevent that.
Did you ever try to balance a slide on an uneven surface? Because stage clips function as a dependable set of hands, gripping the slide securely. This is particularly important if you’re dealing with multiple slides and want them transitioning fast. The clips are strong enough to keep your slides safely in place while you switch.
Stage Controls
Stage controls are the way you make your way around. They let you move the slide directly under the objective. It’s as if you had a GPS for your specimen to lead you to the part that you want to look at.” It’s as if you’ve glimpsed something interesting, but can’t quite get your hands (or eyes) on it. Stage controls save the day.
These controls are not just about movement; they’re about precision. They allow you to make micro-adjustments, that mean the difference between being able to spot critical details or not. Ever find something unexpected in adjusting the stage? That’s how fine-tuning your perspective pays.
Just imagine, if only you could explore the entirety of your specimen with ease… Stage controls let you enjoy that freedom by making your trip a smooth and comfortable exploration.
COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE CARE OF THE MICROSCOPE
The compound light microscope is a vital tool in laboratories. Proper use and care extend its lifespan. Regular maintenance ensures clear, accurate results. Let’s explore daily care and long-term storage tips. These practices will keep your microscope in top condition.
Everyday Use: On Compound Light Microscope Labeled
Protect your lenses for clearer vision and better protection on the job. Dry the lenses with a soft, lint-free cloth. For stubborn spots, wash with lens cleaning solution. Avoid touching lenses with fingers. Fingerprints blur images. Check light source regularly. Replace bulbs when dim. Position the light for best viewing. Don’t let it get too dirty or covered with crap. The clean stage makes a slide move easily.
Long-term Storage
Proper storage protects the microscope. Keep in dust free room. And, when not in use, protect it with a dust jacket. Keep it in a dry area. Humidity can damage optical parts. Use a case to transport it. This prevents knocks and scratches. Check if the case is padded for protection. Keep the microscope locked when not in use. This prevents unauthorized handling. With regular checks, it can stay in a good condition.
Common Applications
A labeled diagram of a compound light microscope helps students understand the various parts. It’s also used in schools and laboratories. This device enlarges tiny objects and renders details visible for scientific observations.
The compound microscope can be a useful instrument in several fields of science. Recognising its usual uses can increase your appreciation of its worth. Whether you’re a student, a scholar or just curious, understanding where and how it’s used can help enhance your appreciation of its significance. Further here are some interesting uses.
Biological Studies
The most common use of compound microscopes is biological research. Such microscopes help scientists get a close-up view of cells, tissues and tiny organisms. Picture yourself looking into the microcosmic realm and finding life’s secret nuances. You will remember (from high school biology) that first excited glimpse of a cell dividing when you looked down the lens of a microscope in biology class. Such visual revelations are essential in understanding diseases and constructing treatments. What ancient questions of cellular life might you answer with a microscope?
Compound Light Microscope in Material Science Labelled diagram of x Use ‘ Click here for mobile version.
Compound light microscopes are for more than biology. They’re also material scientists of sorts. Scientists employ these microscopes to explore the microstructure of metals, polymers and other materials. This is of assistance in understanding material behavior and product design. Consider the smartphone in your hand. This was constructed using high quality materials,probably had a micro-scope used to examine the materials for strength and function. What kind of innovative things would you be able to do with advanced knowledge in material science. Some uses of Compound Light Microscopes The following are some general uses of the compound light microscopes that have made them important in scientific progression. As you think about these fields, consider how you could interface with this technology. Where in your work or study do you see potential for discovery?
Frequently Asked Questions
What Exactly is a compound light microscope?
The compound light microscope uses two or more lenses to produce an enlarged image.
How does a light microscope work?
It directs the light through lenses to amplify a small object so that it can be seen.
What is the magnitude of a simple light microscope in compound microscope?
It’s standard for being able to magnify images of objects up in the 40x-1000x range.
Can you describe the major components of a compound light microscope.
Main components are the eyepiece, objective lens, stage and light source.
How is a light microscope different from an electron microscope?
This is because light microscopes use visible light, while electron microscopes use electrons.
What are the uses of compound light microscope?
It’s user friendly, inexpensive and great for viewing live specimens.
Are bacteria visible with a compound light microscope?
Yes it can see some bacteria, but you will need more magnification to do a bit of detail.
Conclusion About Microscope
The Details of the Compound Light Microscope A compound light microscope shows you a whole lot to explore. Each part plays a vital role. Knowledge of these elements helps you become a better microscopist. The eyepiece, Objective lenses, and Stage are important. They concentrate and amplify your samples. The illuminator sheds light, so you see those little things in full.
It’s those little tweaks that really count! Mastery of the fundamentals adds to your confidence. This is the backdrop against which these things rationalize. You can now view microcosmic organisms with the bare eyes. And what are to be found in this world of little are just waiting for you! Read on to find out more about this interesting tool.
It’s the beginning of your trip into the microcosm.






