
Bluetooth technology has become an integral part of daily life for many of us, myself included. It’s there, quietly humming in the background of your day– pairing your earbuds, your smartwatch, your stereo in the car even (perhaps it will one day extend to that toothbrush you’re using).
But do you ever think about how it all started? Who dreamed up the idea of wirelessly connecting devices and why is it named after a Viking king?
In this article, I will lead you through the fantastic, a little bizarre, and far older than you would think tale of Bluetooth. You’ll hear where it came from, who was behind it, how it works and how it has changed the world as well as where its future is taking us.
The Birth of Bluetooth A 1980s and 1990s Spark
You’d never know it by looking at them, but you could be wearing 21st-century technology in your ears. But its origins go back to the 1980s, when shoulder-pads and cassette-players ruled the world.
It has all come from a bunch of engineers in Ericsson, which is the Swedish telecommunications company. Sometime around 1989, Dr. Nils Rydbeck working with Johan Ullman and later Jaap Haartsen (the lead engineer often referred as the “father of Bluetooth”) began to investigate a new short range wireless communication technology. Their mission? Ditch the rat’s nest of cords that connected phones, headsets and computers.
Personal note: I can still recall getting my old wired headphones untangled on the ride into work in the morning, like solving a Rubik’s Cube made of knots. Bluetooth ended that struggle forever.
By 1994, it had evolved into what we now refer to as Bluetooth technology. Ericsson’s engineers had desired for a universal standard which could enable devices to easily “converse” without the tangled mess of proprietary connectors.

The Invention How the Whole Thing Was Built
Bluetooth’s underlying technology, that of using radio waves in the 2.4 GHz ISM band (the same as your Wi-Fi and microwave oven; they are very polite about sharing) facilitates this transmission.
The genius of Bluetooth lies in frequency hopping, and hopping rapidly from frequency to frequency to try to avoid interference. This was a new technology that was more stable, secure and energy-efficient than previous wireless approaches.
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) – made up of Ericsson, IBM, Intel, Nokia and Toshiba in 1998. This partnership would standardize the technology and bring it to the forefront of popular use.
Late in 1999, the first consumer-grade Bluetooth device a hands-free cellphone headset appeared on the market. It wasn’t glamorous, but a revolution was happening.
So Why the Name-Bluetooth? (Hint: Vikings Were Involved)
This is history with a side of nerd humor. The moniker “Bluetooth” is borrowed from King Harald “Bluetooth” Gormsson, the Viking who united Denmark and Norway much like Computer Hardware connects devices.
The name was put forth by Jim Kardach, an Intel employee who was working on the technology and had read a lot about the Viking king. It was a temporary code name, but it stuck.
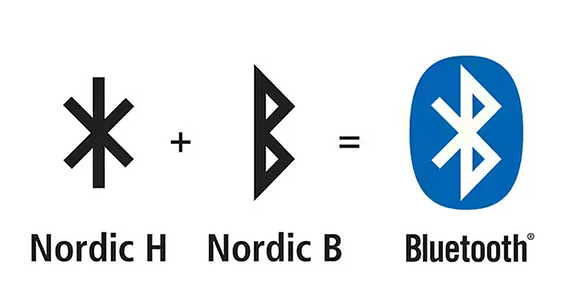
Indeed, even the Bluetooth logo is a combination of two Viking runes that represent King Harald’s initials, H (ᚼ) and B (ᛒ), which are joined together in one symbol.
Fun fact: If a different name had been chosen, Bluetooth might have become known as “PAN” (Personal Area Network). It doesn’t have quite the same ring, does it?
How Bluetooth Has Revolutionized the Way We Connect
The magic of Bluetooth is in its simplicity, universality and low power requirement. It doesn’t take Wi-Fi, data or a complicated setup to make it work. Pair it once, and devices will then recognize each other like old pals.
Common Uses You May Not Know
- Wireless headphones and speakers
- Smartwatches and fitness trackers
- Car infotainment systems
- Key trackers and beacons
- Smart home devices
Today, more than 5 billion Bluetooth-enabled devices are sold each year. There are now over 15 billion Bluetooth connections active around the world, finds bluetooth SIG 2024.
It’s not simply a matter of convenience; it is a question of freedom.
It’s not simply a matter of convenience; it’s a question of freedom. This technology freed us from burdensome cords and chaos-inducing clutter.
Bluetooth 1.0–5.4 Transition
The innovation didn’t stop after the first release. Each new generation brought enhanced capabilities, faster speeds, and greater range, transforming the way devices connect and communicate. Every new generation added capabilities, speed and range.
Version Year Key Feature
1.0 1999 First consumer release
2.0 2004 Enhanced Data Rate (EDR)
3.0 2009 High-speed transfer
4.0 2010 Low Energy (BLE) for IoT
5.0 2016 Greater range, speed, IoT focus
5.4 2023 Better broadcast and energy optimization
When Bluetooth 4.0 Low Energy (BLE) arrived, it was a game changer for wearables and Internet of Things devices. Bluetooth 5. x iterations have since upped its power efficiency and range significantly all the way to 800 feet under ideal conditions.
How Bluetooth Really Works (No, Not the Tech Kind)
Let’s break it down simply:
When you pair your phone to your earbuds, Bluetooth makes use of short-range radio waves and creates a piconet, or personal area network.
One piconet can have one “master” device (say, your phone) and numerous “slaves” (like earbuds or smartwatches or speakers). Devices sync and speak through coded signals which hop frequencies up to 1,600 times a second—dodging interference and eavesdropping.
Personal test: Once I walked around my apartment — phone in one room and Bluetooth speaker in another. No drops. No static. It just worked like magic.
Bluetooth vs. Wi-Fi -Not Enemies, Just Neighbors
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi both exist in The 2.4 GHz range, but they do operate on different standards:
- Bluetooth: Allows the device to attach around Bluetooth (for close range, low power communication – like with cell phones)
- Wi-Fi: High speed long range data intensive (best for internet browsing)
They don’t compete with each other, but complement each other. Between them, both are used by the vast majority of all modern gadgets smartphones and laptops included.
The human side -Bluetooth and its indelible impact on our lives
And apart from the tech specs, Bluetooth transformed how we socialize, travel and even work.
- In cars, it means hands-free calling and streaming (saving relationships as well as tickets).
- In offices, it supplies wireless mice, keyboards and headsets freeing desks from trappings and lifting productivity.
- And in health care, Bluetooth can monitor vitals and transmit that data to doctors in real time.
Bluetooth has been the little-known backbone of the wireless world we take for granted now.
Personal moment: I still smile every time my car immediately gloms on to my phone’s playlist, as if it just knows how much better I am.
Fun Facts You (Probably) Didn’t Know.
- They were very expensive, the first Bluetooth headset was around 150 dollars in 1999.
- There are 38,000+ member companies now in the Bluetooth SIG.
- It has double the speed and four times the range of version 4.2.
- Nearly all cellphones sold today have Bluetooth baked into them.
Challenges and Misconceptions
Despite being a hit, Bluetooth has had its issues, particularly in terms of connection reliability and security.
Earlier models had pairing problems, and hackers could sometimes exploit weaknesses using “bluejacking” or “bluesnarfing.”
But Bluetooth SIG is continuously updating its security protocols. These days, modern devices are based on 128-bit encryption, which means our systems have never been more secure.
The New Face of Bluetooth Smarter, Greener, and Everywhere
Bluetooth is moving towards smarter and more power-efficient networks. The focus areas include:
- Bluetooth LE Audio: Better sound, less power
- Auracast couple cast audio: Share music or translations across several listeners
-
IoT integration: From smart locks to industrial sensors
-
Bluetooth mesh networking: For large-scale smart building systems
Experts predict Bluetooth will be the backbone of the next generation of connected devices, especially in healthcare, automotive, and smart city infrastructures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. When was Bluetooth invented?
Bluetooth’s origins stem from 1994, when Dr. Jaap Haartsen began working at Ericsson. They designed it as a short-range wireless communication alternative to cables, resulting in a global standard connecting billions of devices today.
2. Who invented Bluetooth and why?
Dr. Jaap Haartsen and Sven Mattisson at Ericsson invented Bluetooth to eliminate messy cables between electronic devices. Their breakthrough technology allowed not only phones, but also computers and accessories to connect without wires — changing forever how we engage with tech across the globe.
3. Why is it called Bluetooth?
The name “Bluetooth” is a tribute to King Harald Bluetooth, a Viking ruler who controlled Denmark and Norway. The thing brings devices together the way he brought people together. Its logo consists of two ancient Nordic runes that symbolize his initials, H and B.
4. When did Bluetooth become a Public tech?
Companies began deploying Bluetooth commercially in 1999, and the first wireless headset appeared soon after. Laptops, phones and other electronics soon followed suit, making Bluetooth the ubiquitous wireless connection it is today.
5. What devices use Bluetooth today?
You can find Bluetooth in smartphones, smartwatches, earbuds, cars, speakers, and computers it even powers connectivity in some medical equipment. It links billions of products in more than 100 countries-especially with those increasingly common wireless headphones and earbuds that make everyday tasks such as listening to music or checking your fitness status smoother, quicker, completely cordless.
6. Is Bluetooth technology safe?
Yes. Bluetooth employs frequency hopping across 79 channels and 128-bit encryption to secure data. Newer models are much more secure, but users should maintain their device’s software and not pair them in public to prevent unwanted access or interference.
7. What’s the next version of Bluetooth?
The future of Bluetooth in the BLE and LE Audio developments. These deliver extended-range, battery life and increased sound quality – accelerating the mass adoption of smart homes, connected cars and wearables for a truly wireless world.
Conclusion Vikings and Modern Connections
So, when was Bluetooth invented? The response is 1994 but its tale is greater than a date. It’s a tale of vision, partnership and an idea that evolved into a worldwide standard that links billions of lives.
What began as a means of eliminating a few cords is now connecting everything from earbuds to heart monitors to coffee makers. Bluetooth is one of those discoveries where the smallest innovations have the largest effects.







